Cross-Chain NFT Relayer
This demo is not fully functional at this time. The team is continually developing the gRPC node's capabilities. Thank you for your understanding and continued support.
In this tutorial, we will build a simple dapp with cross-chain NFT authentication using the relayer feature. An off-chain relayer will validate NFT ownerships from another blockchain, and only NFT owners can write to WeaveDB. By default, WeaveDB authenticates users with crypto accounts, but in this dapp, cross-chain NFTs will be used for the authentication.
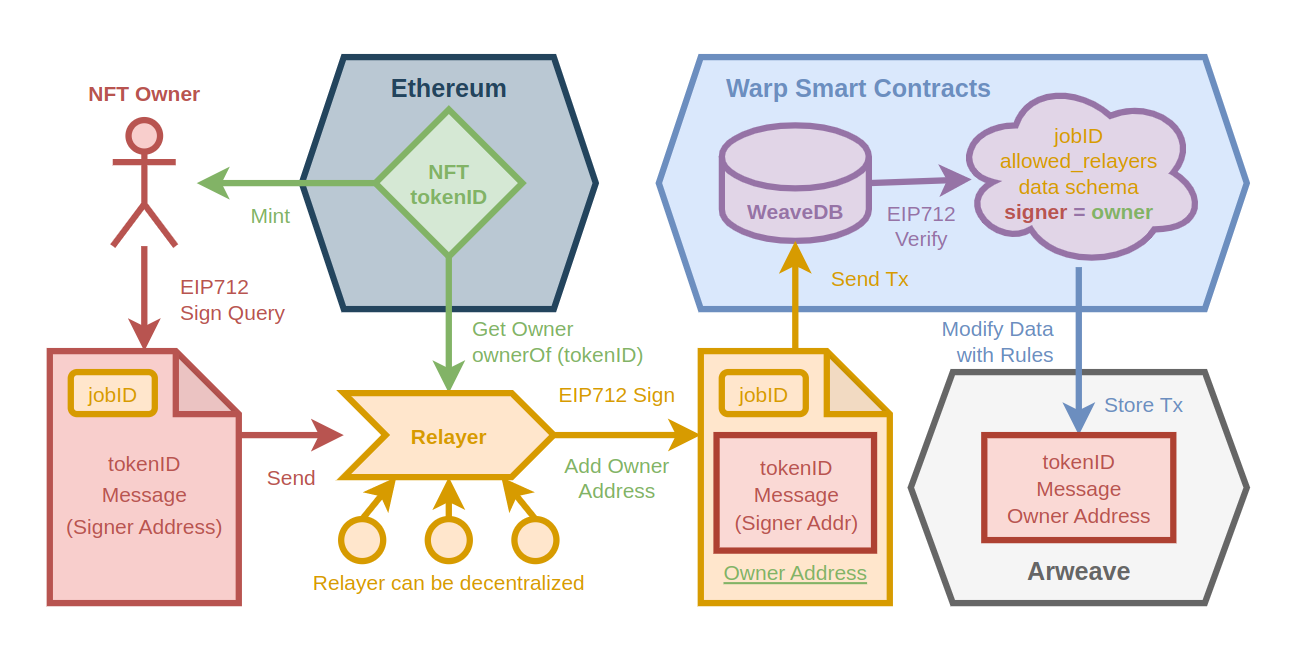
- A relayer job can be preset on the WeaveDB instance with
jobId,allowed_relayers,extra data schema. All the conditions must be met before relayed queries go through. - The NFT owner mints an NFT.
- The owner signs query data (
tokenID,Message) with eip712 and sends it to the relayer withjobID. Thesigner addresscan be later obtained by verifying the eip712 signature. - The relayer checks the owner of the
tokenIDand add theowneraddress to the signed query, then signs it with eip712 and send the transaction to the WeaveDB contract on Warp. - The WeaveDB contract verifies the eip712 signatures and validates
jobID,allowed relayersandextra data schema.owneris the extra data to be validated. - The original query data (
tokenID,Message) can be modified with access control rules on the collection. We will check if thesigneris theowner, and if so, add theownerfield to the original data.
In practice, the relayer could/should be decentralized. But we are going to set up a centralized relayer for this demo.
A demo dapp with a test NFT contract on Goerli testnet (opens in a new tab) is deployed at relayer-one.vercel.app (opens in a new tab) where you can free-mint NFTs and post messages via WeaveDB by authenticate with your Goerli NFTs.
Frontend Dapp
Clone the Repo
git clone https://github.com/weavedb/weavedb.git
cd weavedb
yarnDeploy NFT
Before working on the DB, let's deploy a simple NFT contract to the Goerli testnet (opens in a new tab).
If you have no GoerliETH, here's a list of faucets (opens in a new tab).
This is a simple full-on-chain NFT with a free mint function.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Strings.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Base64.sol";
contract NFT is ERC721URIStorage {
using Strings for uint256;
using Counters for Counters.Counter;
Counters.Counter private _tokenIds;
constructor() ERC721("NFT", "NFT") {}
function mint() public returns (uint256) {
uint256 newId = _tokenIds.current();
_mint(msg.sender, newId);
_tokenIds.increment();
return newId;
}
function getTokenURI(uint256 tokenId) public pure returns (string memory){
bytes memory dataURI = abi.encodePacked(
'{',
'"name": "NFT #', tokenId.toString(), '"',
'}'
);
return string(
abi.encodePacked(
"data:application/json;base64,",
Base64.encode(dataURI)
)
);
}
}Go to the NFT folder and install dependencies.
cd examples/relayer-nft/nft-contract
yarnCreate .env file with the following variables.
EVM_RPC="https://goerli.infura.io/v3/yourapikey"
ETHERSCAN_API_KEY="yourapikey"
PRIVATEKEY="yourprivatekey"Compile the contract.
npx hardhat compileThen deploy the contract to the Goerli testnet.
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network goerliNow you should receive your contract address. To verify the contract on Etherscan, run the following.
npx hardhat verify --network goerli YOUR_CONTRACT_ADDRESSDeploy WeaveDB Contracts
cd ../../../
node scripts/generate-wallet.js mainnet
yarn deployOr you could follow this guide and use the Web Console (opens in a new tab).
Now you should receive contractTxId for the deployed contract.
Configure DB Instance
We will show you one command script to set up everything in the end, but these are what needs to be set up.
Set up Data Schema
We are going to set up only 1 collection.
nft: an NFT registry with messages
const schema = {
type: "object",
required: ["owner", "text", "tokenID"],
properties: {
owner: {
type: "string",
},
text: {
type: "string",
},
tokenID: {
type: "number",
},
},
}
await db.setSchema(schema, "nft", { ar: wallet })tokenID: NFT tokenIDowner: NFT owner addresstext: text message
Set up Relayer Job
Set a simple relayer job.
relayerAddress: an EVM address of the relayer to check the Ethereum blockchain and relay WeaveDB queries.schema: JSON schema for the additional data to be attached by the relayer. The relayer will attach only one extra data of string.jobID: our arbitrary jobID will benft.
const job = {
relayers: [relayerAddress],
schema: {
type: "string",
},
}
await sdk.addRelayerJob("nft", job, {
ar: wallet,
})With these simple settings, we expect the relayer to receive an NFT-tokenID, and check the owner address on the Ethereum blockchain (Goerli), then relay the signed WeaveDB query with extra data of string owner address.
Set up Access Control Rules
The NFT ownerships can be verified with Access Control Rules.
const rules = {
let: {
owner: ["toLower", { var: "request.auth.extra" }],
"resource.newData.owner": { var: "owner" },
},
"allow write": {
"==": [{ var: "request.auth.signer" }, { var: "owner" }],
},
}
await sdk.setRules(rules, "nft", {
ar: wallet,
})Set up Everything with Script
To set up everything with one command, run the following.
node scripts/nft-setup.js mainnet mainnet YOUR_CONTRACT_TX_ID RELAYER_EVM_ADDRESSSet up Local gRPC Node
For a better performance for the relayer, you would want to set up a local grpc node.
Make sure docker and docker-compose are installed on your machine.
If you are on Ubuntu, the following commands would install them.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker.io
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.2.3/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composeThen create weavedb.config.js to /grpc-node/node-server directory.
module.exports = {
contractTxId: "xxxxxxxx..."
}Then run docker-compose with yarn run-node.
yarn run-nodeNow you should be able to access the node at localhost:8080.
NextJS Frontend Dapp
We are going to build the front end dapp using NextJS (opens in a new tab) and also set up the relayer as a serverless api.
Create NextJS Project
Set up a NextJS project with the app name relayer-nft.
yarn create next-app relayer-nft
cd relayer-nft
yarn devNow your dapp should be running at localhost:3000 (opens in a new tab).
For simplicity, we will write everything in one file at /page/index.js.
Install Dependencies
Open a new terminal and move to the root directory to continue development.
We use these minimum dependencies.
- WeaveDB Client - to connect with the gRPC node from browsers
- WeaveDB Node Client - to connect with the gRPC node from the serverless api
- Ramda.js (opens in a new tab) - functional programming utilities
- Chakra UI (opens in a new tab) - UI library
- Ethers.js (opens in a new tab) - to connect with Metamask
yarn add ramda weavedb-client weavedb-node-client ethers @chakra-ui/react @emotion/react@^11 @emotion/styled@^11 framer-motion@^6Copy NFT ABI
Copy and save the minimum ABI for the NFT contract to /lib/NFT.json.
The relayer needs this ABI to access the Ethereum blockchain.
[
{
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "tokenId",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"name": "ownerOf",
"outputs": [
{
"internalType": "address",
"name": "",
"type": "address"
}
],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
}
]You need to make /lib directory.
mkdir lib
touch lib/NFT.jsonThen copy the content above to NFT.json.
Set up Environment Variables
Create .env.local file and set the following variables.
EVM_RPC="https://goerli.infura.io/v3/your_api_key"
WEAVEDB_RPC_NODE="localhost:8080"
RELAYER_PRIVATEKEY="Relayer_EOA_Privatekey"
NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_CONTRACT_TX_ID="Your_Contract_Tx_Id"
NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDR="Goerli_NFT_Contract_Address"
NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_RPC_WEB="http://localhost:8080"Set up Relayer
We will set up the relayer as NextJS serverless api located at /pages/api/ownerOf.
The relayer receives signed parameters from frontend users and checks the owner of the NFT with tokenID embedded in the parameters, then relays the DB query with an additional data of owner attached to the query.
const { Contract, providers } = require("ethers")
const provider = new providers.JsonRpcProvider(process.env.EVM_RPC)
const contractTxId = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_CONTRACT_TX_ID
const nftContractAddr = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDR
const SDK = require("weavedb-node-client")
const abi = require("../../lib/NFT.json")
export default async (req, res) => {
const params = JSON.parse(req.body)
const tokenID = params.query[0].tokenID
let owner = "0x"
try {
owner = await new Contract(nftContractAddr, abi, provider).ownerOf(tokenID)
} catch (e) {
res.status(200).json({
success: false,
})
return
}
const sdk = new SDK({
contractTxId,
rpc: process.env.WEAVEDB_RPC_NODE,
})
const tx = await sdk.relay(params.jobID, params, owner, {
jobID: params.jobID,
privateKey: process.env.RELAYER_PRIVATEKEY,
})
res.status(200).json(tx)
}The App Page
The app page /pages/index.js is rather simple.
Import Libraries
Import necessary libraries. We are going to use a bunch of RamdaJS (opens in a new tab) functions for utilities and Chakra (opens in a new tab) for UI.
import SDK from "weavedb-client"
import { ethers } from "ethers"
import { useEffect, useState } from "react"
import {
reverse,
compose,
sortBy,
values,
assoc,
map,
indexBy,
prop,
} from "ramda"
import { Button, Box, Flex, Input, ChakraProvider } from "@chakra-ui/react"Define Variables
let sdk
const contractTxId = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_CONTRACT_TX_ID
const nftContractAddr = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDR
export default function Home() {
const [nfts, setNFTs] = useState([])
const [posting, setPosting] = useState(false)
}nfts: to store messages from NFT holdersposting: to set a flag when message posting is ongoing
Set up Reactive Effect
Initialize the SDK and fetch messages from the gRPC node.
useEffect(() => {
;(async () => {
const _sdk = new SDK({
contractTxId,
rpc: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_RPC_WEB,
})
sdk = _sdk
setNFTs(await _sdk.get("nft", ["tokenID", "desc"]))
})()
}, [])Header
Header View
![]()
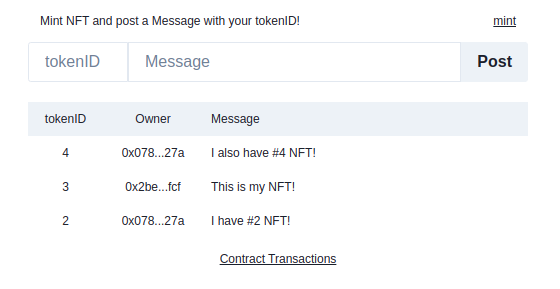
The Header is just a link to the NFT contract on Etherscan and shows posting status when posting a message.
const Header = () => (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" p={3}>
<Box flex={1}>
{posting
? "posting..."
: "Mint NFT and post a Message with your tokenID!"}
</Box>
<Box
as="a"
target="_blank"
sx={{ textDecoration: "underline" }}
href={`https://goerli.etherscan.io/token/${nftContractAddr}#writeContract`}
>
mint
</Box>
</Flex>
)Footer
Footer View
![]()
The Footer is just a link to the Warp contract page on Sonar. So users can view transactions. Nothing special.
const Footer = () => (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" p={3}>
<Box
as="a"
target="_blank"
sx={{ textDecoration: "underline" }}
href={`https://sonar.warp.cc/?#/app/contract/${contractTxId}`}
>
Contract Transactions
</Box>
</Flex>
)
Post
Post View

The Post component lets you post a message with your tokenIDs, and this is where the business takes place.
const Post = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState("")
const [tokenID, setTokenID] = useState("")
return (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" mb={5}>
<Input
disabled={posting}
w="100px"
placeholder="tokenID"
sx={{ borderRadius: "3px 0 0 3px" }}
value={tokenID}
onChange={e => {
if (!Number.isNaN(+e.target.value)) {
setTokenID(e.target.value)
}
}}
/>
<Input
disabled={posting}
flex={1}
placeholder="Message"
sx={{ borderRadius: "0" }}
value={message}
onChange={e => {
setMessage(e.target.value)
}}
/>
<Button
sx={{ borderRadius: "0 3px 3px 0" }}
onClick={async () => {
if (!posting) {
if (tokenID === "") {
alert("enter your tokenID")
return
}
if (/^\s*$/.test(message)) {
alert("enter message")
return
}
setPosting(true)
try {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(
window.ethereum,
"any"
)
await provider.send("eth_requestAccounts", [])
const addr = await provider.getSigner().getAddress()
const params = await sdk.sign(
"set",
{ tokenID: +tokenID, text: message },
"nft",
tokenID,
{
wallet: addr,
jobID: "nft",
}
)
const res = await fetch("/api/ownerOf", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(params),
}).then(v => v.json())
if (!res.success) {
alert("Something went wrong")
} else {
setMessage("")
setTokenID("")
setNFTs(
compose(
reverse,
sortBy(prop("tokenID")),
values,
assoc(res.docID, res.doc),
indexBy(prop("tokenID"))
)(nfts)
)
}
} catch (e) {
alert("something went wrong")
}
setPosting(false)
}
}}
>
Post
</Button>
</Flex>
)
}Inside onClick Function
There are 2 key parts inside the onClick function.
sign method signs a query and creates an object(param) ready to be sent to the relayer. In this code, we are setting the object { tokenID: +tokenID, text: message } to tokenID doc of nft collection. jobID also needs to be specified when signing to relay a query.
const params = await sdk.sign(
"set",
{ tokenID: +tokenID, text: message },
"nft",
tokenID,
{
wallet: addr,
jobID: "nft",
}
)Now send the signed object to the relayer we set up at /api/ownerOf. The relayer is going to check the owner of the tokenID and relay the query with an additional owner data.
The access control rules previously set will make sure the signer is the owner, and only let messages posted if it's true.
const res = await fetch("/api/ownerOf", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(params),
}).then(v => v.json())Messages
Messages View
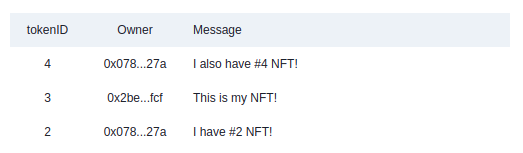
The Messages component loops through nfts and list the messages with a link to the owner page on Etherscan.
const Messages = () => (
<Box>
<Flex bg="#EDF2F7" w="500px">
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="75px">
tokenID
</Flex>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="100px">
Owner
</Flex>
<Box p={2} flex={1}>
Message
</Box>
</Flex>
{map(v => (
<Flex
sx={{ ":hover": { bg: "#EDF2F7" } }}
w="500px"
as="a"
target="_blank"
href={`https://goerli.etherscan.io/token/${nftContractAddr}?a=${v.owner}`}
>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="75px">
{v.tokenID}
</Flex>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="100px">
{v.owner.slice(0, 5)}...{v.owner.slice(-3)}
</Flex>
<Box p={2} flex={1}>
{v.text}
</Box>
</Flex>
))(nfts)}
</Box>
)Return Components
Now return all the components wrapped by <ChakraProvider> tag for UI.
return (
<ChakraProvider>
<Flex direction="column" align="center" fontSize="12px">
<Header />
<Post />
<Messages />
<Footer />
</Flex>
</ChakraProvider>
)The Complete Code
You can also access the entire code on Github (opens in a new tab).
import SDK from "weavedb-client"
import { ethers } from "ethers"
import { useEffect, useState } from "react"
import {
reverse,
compose,
sortBy,
values,
assoc,
map,
indexBy,
prop,
} from "ramda"
import { Button, Box, Flex, Input, ChakraProvider } from "@chakra-ui/react"
let sdk
const contractTxId = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_CONTRACT_TX_ID
const nftContractAddr = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDR
export default function Home() {
const [nfts, setNFTs] = useState([])
const [posting, setPosting] = useState(false)
useEffect(() => {
;(async () => {
const _sdk = new SDK({
contractTxId,
rpc: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_WEAVEDB_RPC_WEB,
})
sdk = _sdk
setNFTs(await _sdk.get("nft", ["tokenID", "desc"]))
})()
}, [])
const Header = () => (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" p={3}>
<Box flex={1}>
{posting
? "posting..."
: "Mint NFT and post a Message with your tokenID!"}
</Box>
<Box
as="a"
target="_blank"
sx={{ textDecoration: "underline" }}
href={`https://goerli.etherscan.io/token/${nftContractAddr}#writeContract`}
>
mint
</Box>
</Flex>
)
const Footer = () => (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" p={3}>
<Box
as="a"
target="_blank"
sx={{ textDecoration: "underline" }}
href={`https://sonar.warp.cc/?#/app/contract/${contractTxId}`}
>
Contract Transactions
</Box>
</Flex>
)
const Post = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState("")
const [tokenID, setTokenID] = useState("")
return (
<Flex justify="center" width="500px" mb={5}>
<Input
disabled={posting}
w="100px"
placeholder="tokenID"
sx={{ borderRadius: "3px 0 0 3px" }}
value={tokenID}
onChange={e => {
if (!Number.isNaN(+e.target.value)) {
setTokenID(e.target.value)
}
}}
/>
<Input
disabled={posting}
flex={1}
placeholder="Message"
sx={{ borderRadius: "0" }}
value={message}
onChange={e => {
setMessage(e.target.value)
}}
/>
<Button
sx={{ borderRadius: "0 3px 3px 0" }}
onClick={async () => {
if (!posting) {
if (tokenID === "") {
alert("enter your tokenID")
return
}
if (/^\s*$/.test(message)) {
alert("enter message")
return
}
setPosting(true)
try {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(
window.ethereum,
"any"
)
await provider.send("eth_requestAccounts", [])
const addr = await provider.getSigner().getAddress()
const params = await sdk.sign(
"set",
{ tokenID: +tokenID, text: message },
"nft",
tokenID,
{
wallet: addr,
jobID: "nft",
}
)
const res = await fetch("/api/ownerOf", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(params),
}).then(v => v.json())
if (!res.success) {
alert("Something went wrong")
} else {
setMessage("")
setTokenID("")
setNFTs(
compose(
reverse,
sortBy(prop("tokenID")),
values,
assoc(res.docID, res.doc),
indexBy(prop("tokenID"))
)(nfts)
)
}
} catch (e) {
alert("something went wrong")
}
setPosting(false)
}
}}
>
Post
</Button>
</Flex>
)
}
const Messages = () => (
<Box>
<Flex bg="#EDF2F7" w="500px">
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="75px">
tokenID
</Flex>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="100px">
Owner
</Flex>
<Box p={2} flex={1}>
Message
</Box>
</Flex>
{map(v => (
<Flex
sx={{ ":hover": { bg: "#EDF2F7" } }}
w="500px"
as="a"
target="_blank"
href={`https://goerli.etherscan.io/token/${nftContractAddr}?a=${v.owner}`}
>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="75px">
{v.tokenID}
</Flex>
<Flex justify="center" p={2} w="100px">
{v.owner.slice(0, 5)}...{v.owner.slice(-3)}
</Flex>
<Box p={2} flex={1}>
{v.text}
</Box>
</Flex>
))(nfts)}
</Box>
)
return (
<ChakraProvider>
<Flex direction="column" align="center" fontSize="12px">
<Header />
<Post />
<Messages />
<Footer />
</Flex>
</ChakraProvider>
)
}Using the Dapp
Using the Dapp
When minting the NFT, please use a different EVM account from the relayer. This is because if the relayer and the message sender are the same account, they will have the same nonce for separate signatures and it will cause a signature verification error.